We all know vegetables and fruits are beneficial for our health. Including more vegetables and fruits in a healthy diet can reduce the risk of some chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and overweight and obesity. Scientific studies have also linked human productive health with diet pattern and lifestyle. Most countries have dietary recommendations that include fruits and vegetables. USDA 2015-2020 dietary guidelines recommend eating half plate vegetables and fruits.
Vegetables and fruits, such as kale, spinach, beans, tomato, carrot, orange, and avocado are important sources of micro-nutrients (antioxidants, potassium, iron, zinc, magnesium, selenium, Vitamin A, Vitamin E, Vitamin B). Some vegetables and fruits such as olive, avocado, and potato carry about 10% monounsaturated fatty acids, which has powerful health benefits. Vegetable and fruits are also good dietary fiber sources.
Micro-nutrients
Positive effects of micronutrients on the human reproductive health of both man and women have been widely confirmed.
- Folate (vitamin B9) helps red blood cells formation. It is important in facilitating regular, healthy ova production and helping to prevent neural tube defects during early pregnancy. Arrowroot, seaweed, and collard green vegetables are significant sources of folate.
- Deficiencies of vitamin A, D, E are responsible for inhibits several human body functions, including men and women fertility function.
- Antioxidants such as polyunsaturated fatty acids, flavonoids, vitamin A, vitamin E, and CoQ10 can work as a reductant to prevent oxidative damage. CoQ10 is known as an antioxidant protecting egg and sperms.
- Vegetables and fruits are important sources of myo-inositol, which is an insulin-sensitizing agent and may promote healthy ovulation. Myo-inositol is currently used to treat polycystic ovary syndrome. Nuts, citrus fruits, and green collard vegetables are the important inositol sources.
Vegetables and fruits intake as part of healthy diet closely relates to human reproductive health. Recent researches ( 1, 2, 3, 4 ) on the impacts of diet on male fertility revealed that vegetables and fruits such as kale, lettuce, carrot, tomato and orange improve male semen quality.
A Harvard University study carried out in a healthy male population found a positive linear relation between dietary carotenoids (beta-carotene and lutein), lycopene intake and semen quality. Based on USDA Food Composition Databases, beta-carotene mainly exists in sweet red pepper, carrot, sweet potato, dandelion greens, kale, spinach, pumpkin. Lutein mainly exists in kale, spinach, sweet potato leaves, dandelion greens, turnip greens, cress, chard, collard. Lycopene mainly exists in tomato, guava, watermelon, papaya, grapefruit.
2018 published study of food consumption and risk of endometriosis suggests that higher intake of fruits, particularly citrus fruits, are associated with lower risk of endometriosis, which is a hormone-dependent disorder affects 10% of the reproductive women. Endometriosis often associates with infertility. Beta-cryptoxanthin in citrus fruits may play an important role in this association. Inositol level is also high in citrus fruits.
Plant fats
Fats play important roles for all functions of human body. It is an important part of a healthy diet. Olive, and avocado carry about 10% of monounsaturated fatty acids, which have protective effects to human body. As stated by mono, monounsaturated fatty acids have only one double carbon bond in their chemical structure. Plant and animals may both provide sources of monounsaturated fatty acids.
Most common monounsaturated fatty acid occurs in food sources is oleic acid. Its protective effects on heart diseases, type 2 diabetes, ulcerative colitis and stroke have been verified by numerical studies. Oleic acid may affect baby development and women reproductive health.
- Oleic acid is one of the important brain fat compositions. The higher oleic acid level in the brain is found to associate with positive personality traits in adolescent boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- A 2018 review concluded that available data suggest that oleic acid can contribute to the normal oocyte and preimplantation embryo development, and it may play a significant role in oocyte and early embryo development.
Although oleic acid can be produced in the human body, its production might be limited by different conditions. Sufficient oleic acid intake from food sources is important for maintaining the adequate oleic acid level to ensure normal organ functions.
Dietary fiber and carbohydrates
Fruits and vegetables are good sources of dietary fiber and other carbohydrates ( sugars, starches, sugar alcohols). Dietary fiber is the type of carbohydrates that the human body can’t digest and absorb fiber. Other carbohydrates contribute to energy intake.
Dietary fiber from vegetable and fruits may
- help reduce blood cholesterol levels, lower risk of heart disease
- help to maintain bowel health, and reduce constipation which is a common problem in pregnancy.
- slow digestion and results in a more steady and lower blood sugar level, which help to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- aids in achieving a healthy weight by providing a feeling of fullness with fewer calories.
Research studies have linked infertility with high cholesterol level, high blood sugar level, diabetes, and obesity. More intake of dietary fiber may help to improve reproductive health and promote a healthier pregnancy. Fruit juices contain high-level of free sugar and very low fiber are not as healthy as whole fruits.
In conclusion, including an adequate amount of vegetables and fruits with higher levels of beneficial nutrients in your diet could help to improve productive health. A chart of USDA recommendations of vegetables and fruits intake at 2000 calories level is attached below.
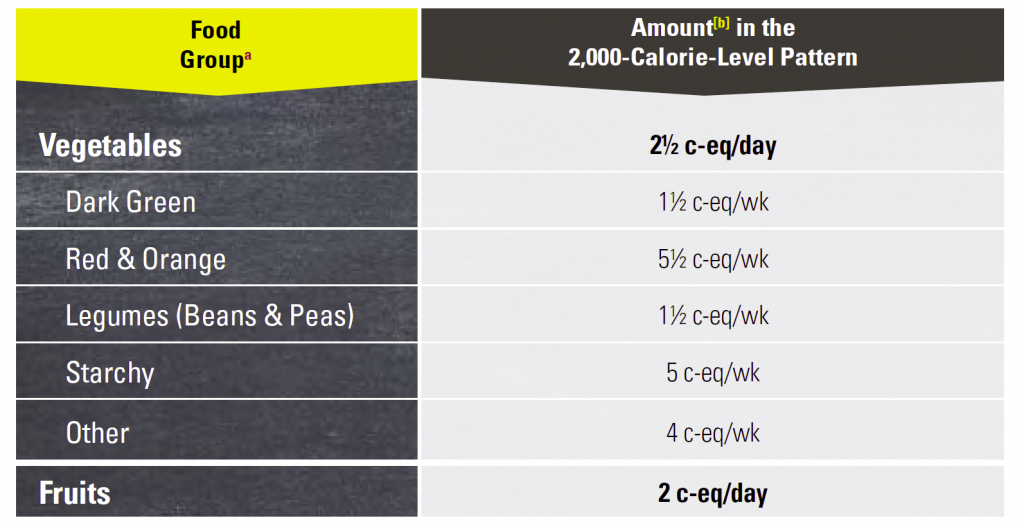
C in above chart stands for Cup
