Fish, Meat, dairy products and eggs are our major dietary sources of protein and important sources of fats. Although protein and fats can be obtained from both plant and animal sources, animal-based foods are unreplaceable by plant-based.
Animal protein vs plant protein
Protein is one of the major energy sources in our diet. The human body needs 22 specific amino acids to build proteins for varies organs and functions, such as muscles, red blood cells. With the fact that human body can only produce 13 amino acids on its own, obtaining 9 other types from diet is necessary.
Some of these 9 types of amino acids can be found in plant sources, but all could be obtained from animal sources, such as meat, egg, fish and dairy products. Animal proteins – the complete protein that containing all of the essential amino acids is one of the most important macronutrients human body needed to function effectively.
Soybean protein may be considered as a complete protein. However, 2 out of 9 essential amino acids are found in only small amounts which are significantly lower than animal source proteins. It is not recommended to replace animal-source protein completely with soybean.
Animal Fats
We have discussed the oil and fats in previous posts (Fruit and Vegetables, Fats and oils, Omega-6, Saturated Fats, Trans fats).
It is known that human reproductive health largely relies on fats. According to this USDA food data system, 38% of fats American consume is from direct animal sources food (does not include added fats and oils), 53% is from added fats and oils, which are mainly plant fats and saturated animal fats. When consuming fat, we prefer good fats - unsaturated fat to neutral fats - saturated and want to avoid bad fats – trans fats. Well balanced healthy fats consumption can promote optimal reproductive health and may help to reverse both male and female infertility issues.
Unsaturated animal fats
Unsaturated acids can promote human reproductive system health, including ovulation, pregnancy health, fetus development, male sperm fertility ability.
Oleic acid is the major form of monounsaturated fatty acids exists in animal sources foods. Egg yolk and chicken are preferred animal sources of oleic acid. Although beef and port fats also contain notable amounts of oleic acid, red meats also contain a high level of saturated fats which is not as healthy as unsaturated fats.
Long chain omega-3 fatty acids (DHA and EPA) are one of the most beneficial fats for reproductive system found in animals. Fish is the type of food containing most long chain omega-3 especially DHA and EPA and low in omega-6. Increasing fish consumption helps reduce omega-6 to omega-3 ratios, which is at an unhealthily high level in the American diet. According to USDA Food Composition Database, following fishes contain a high level of omega-3.
- Mackerel
- roe
- shad
- salmon
- sablefish
- whitefish
- anchovy
- tuna
Mercury contamination in Fish
However, some fish and shellfish contain higher levels of mercury that may harm an unborn baby or young child's developing nervous system. It is advised to choose fishes that is low in mercury for diet. Mercury levels in some species of commercial fish and shellfish are monitored by FDA, you may find it here. Following is the FDA recommendations for choosing fish,
- Do not eat Shark, Swordfish, King Mackerel, or Tilefish because they contain high levels of mercury.
- Eat up to 12 ounces (2 average meals) a week of a variety of fish and shellfish that are lower in mercury.
- Five of the most commonly eaten fish that are low in mercury are shrimp, canned light tuna, salmon, pollock, and catfish.
- Another commonly eaten fish, albacore ("white") tuna has more mercury than canned light tuna. So, when choosing your two meals of fish and shellfish, you may eat up to 6 ounces (one average meal) of albacore tuna per week.
- Check local advisories about the safety of fish caught by family and friends in your local lakes, rivers, and coastal areas. If no advice is available, eat up to 6 ounces (one average meal) per week of fish you catch from local waters, but don't consume any other fish during that week.
Follow these same recommendations when feeding fish and shellfish to your young child but serve smaller portions.
Saturated fats and trans fats
Fats from red meats and dairy products are mainly saturated fats. They are neutral to human health. In order to guarantee sufficient unsaturated fatty acids intake, it is recommended to limit saturated fats intake. USDA 2015 to 2020 dietary guidelines for American recommend consuming less than 10% off daily energy from saturated fats. Based on 2000 calories diet, 10% equivalent to 20 grams. When reading the product label, remember that
- 5% DV or less of saturated fat per serving is low
- 20% DV or more of saturated fat per serving is high
The fat contents of Beef and lamb are the foods containing most natural trans fats. Although effects of natural trans-fats on human health are still not well studied, we still recommend limiting beef and lamb intake.
Micronutrients
Animal sources foods also packed with micronutrients. Some of the micronutrients in animal sources foods can well compensate the density in plant foods, such as vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, and zinc.
Vitamin B12 is a micronutrient essential for cellular growth, differentiation, and development. Studies showed deficiency of vitamin B12 in pregnancy may result in low birth weight and communicable diseases in children. Vitamin B12 is mainly found in fish, meat, poultry and dairy products. Many people who avoid animal foods are deficient in Vitamin B12.
Our recommendations
In conclusion, animal source foods are necessary for us to obtain nutrient that does not have sufficient density in plant foods. We recommend to
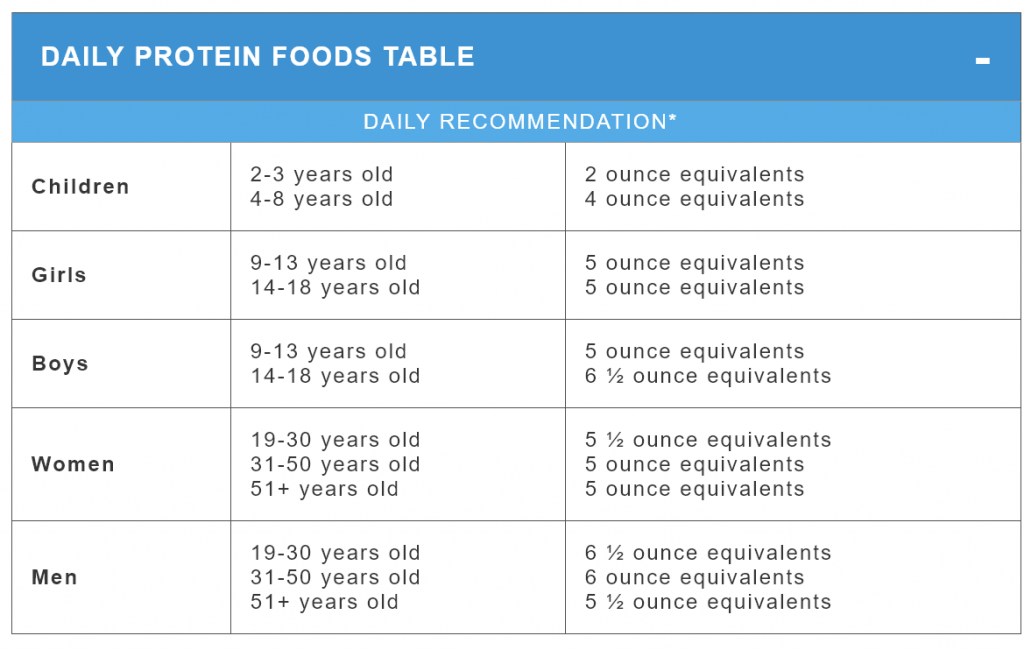
- Consume an adequate amount of animal source foods including both protein and fats. Animal protein and fats are both essential for human body. Diet including proper amount animal source foods could help us improve reproductive health. Following charts presents USDA recommended protein food intake,
- Include 2 of 4 oz serving of fish in your diet every week. Fish is an ideal food rich in high quality protein, high level unsaturated fats especially omega-3 fatty acids (DHA, EPA) and micronutrients, low in trans fats and saturated fats.
- Reduce red meat and related product intake and replaced it with more healthier options such as fish, shrimp, chicken, and duck.
- Choose a healthy cooking oil for your diets such as olive oil, peanut oil, and canola oil.
- Limit dining out. Reduce unhealthy cooking oil intake to cut trans fats, saturated fats intake, and balance a healthier omega-3/omega-6 ratio.
- Read package labels for processed foods to avoid/reduce unhealthy ingredients.
About 0.5% of US adults are vegans, consume animal foods are not realistic for this population. It is recommended to include a large variety of plant foods to provide the body with complete essential amino acids. Omega-3 supplements are also recommended for vegetarians and vegans.